Part 3: Blueprint
What Will You Do¶
In this part of the self-paced exercise, you will create a custom cluster blueprint with a Karpenter add-on, based on declarative specifications.
Step 1: Create Namespace¶
In this step, you will create a namespace for Karpenter. The "namespace.yaml" file located in
The following items may need to be updated/customized if you made changes to these or used alternate names.
- value: karpenter-cluster
kind: ManagedNamespace
apiVersion: config.rafay.dev/v2
metadata:
name: karpenter
description: namespace for karpenter
labels:
annotations:
spec:
type: RafayWizard
resourceQuota:
placement:
placementType: ClusterSpecific
clusterLabels:
- key: rafay.dev/clusterName
value: karpenter-cluster
- Open Terminal (on macOS/Linux) or Command Prompt (Windows) and navigate to the folder where you forked the Git repository
- Navigate to the folder "
/getstarted/karpenter/namespace" - Type the command below. Be sure to update the project name with the name of your project.
rctl create namespace -f namespace.yaml -p <project-name>
If you did not encounter any errors, you can optionally verify if everything was created correctly on the controller.
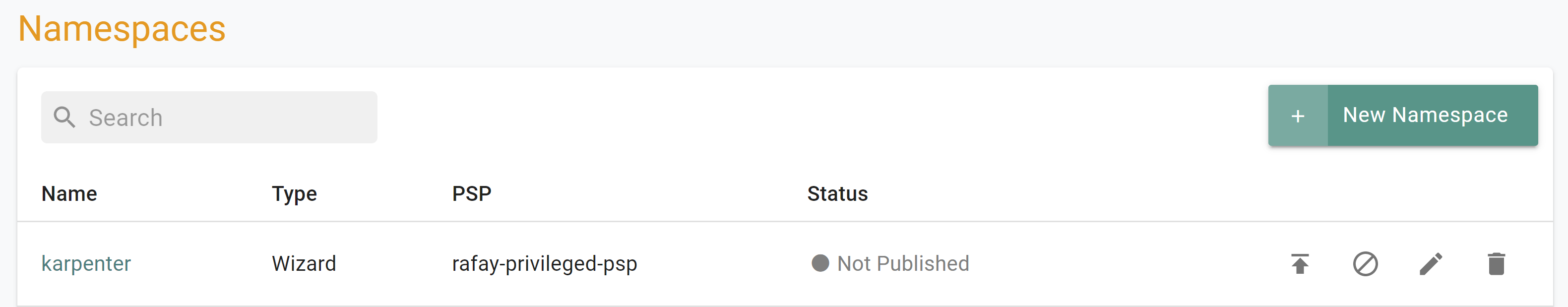
- Navigate to the "defaultproject" project in your Org
- Select Infrastructure -> Namespaces
- You should see an namesapce called "karpenter"
Step 2: Create Addons¶
In this step, you will create two custom addons, one for the Karpenter Controller and a second for the Karpenter NodePool and EC2NodeClass. The specification files for this section are located in
The following details are used to build the Karpenter addon declarative specification.
- "v1" because this is our first version
- The addon is part of the "defaultproject"
- Name of addon is "karpenter-addon"
- The addon will be deployed to a namespace called "karpenter"
- You will be using a "custom-values.yaml" as an override which is located in the folder "
/getstarted/karpenter/addon"
apiVersion: infra.k8smgmt.io/v3
kind: Addon
metadata:
name: karpenter-addon
project: karpenter
spec:
artifact:
artifact:
catalog: default-rafay
chartName: karpenter
chartVersion: 1.0.1
valuesPaths:
- name: file://custom-values.yaml
options:
maxHistory: 1
timeout: 1m0s
type: Helm
namespace: karpenter
sharing:
enabled: false
version: v1
- Open Terminal (on macOS/Linux) or Command Prompt (Windows) and navigate to the folder where you forked the Git repository
- Navigate to the folder "
/getstarted/karpenter/addon" - Type the command below
rctl apply -f karpenter-addon.yaml
If you did not encounter any errors, you can optionally verify if everything was created correctly on the controller.
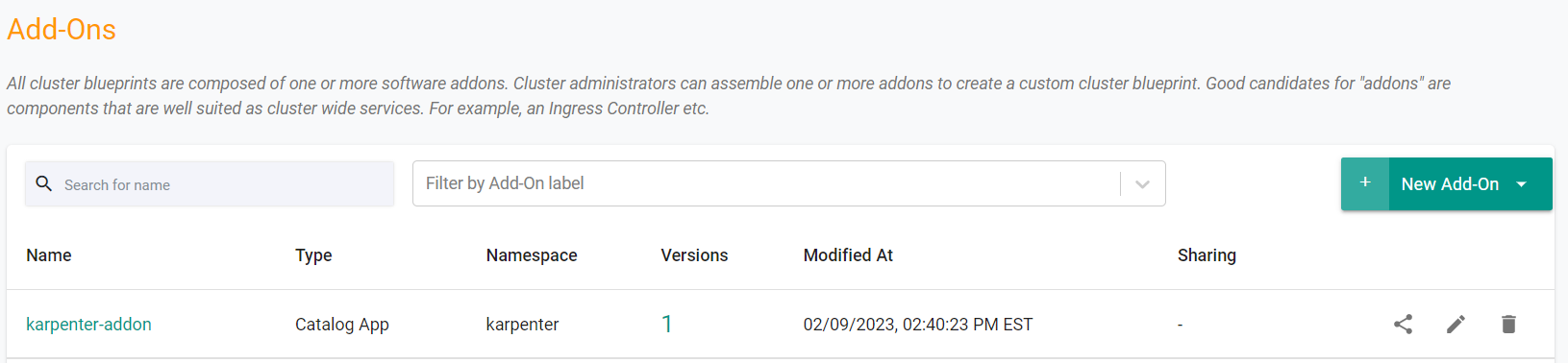
- Navigate to the "defaultproject" project in your Org
- Select Infrastructure -> Addons
- You should see an addon called "karpenter-addon"
Next, we will create the second custom addon for the Karptenter NodePool and EC2NodeClass.
Note that the name of the role we are using was created in Part 1.
Note that the "cluster-name" is set to match the name of the cluster and the AWS tags that were specified in the cluster spec file.
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1
kind: NodePool
metadata:
name: default
spec:
template:
spec:
requirements:
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values: ["amd64"]
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values: ["linux"]
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["spot"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-category
operator: In
values: ["t"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-generation
operator: Gt
values: ["2"]
nodeClassRef:
group: karpenter.k8s.aws
kind: EC2NodeClass
name: default
limits:
cpu: 1000
disruption:
consolidationPolicy: WhenEmptyOrUnderutilized
budgets:
- nodes: "100%"
reasons:
- "Empty"
- "Drifted"
expireAfter: 720h # 30 * 24h = 720hconsolidateAfter: 1m
consolidateAfter: 1m
---
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1
kind: EC2NodeClass
metadata:
name: default
spec:
amiSelectorTerms:
- alias: al2@latest
tags:
email: [email protected]
env: dev
role: "KarpenterNodeRole-Rafay"
subnetSelectorTerms:
- tags:
cluster-name: "{{{ .global.Rafay.ClusterName }}}"
securityGroupSelectorTerms:
- tags:
cluster-name: "{{{ .global.Rafay.ClusterName }}}"
The following details are used to build the provisioner addon declarative specification.
- "v1" because this is our first version
- The addon is part of the "defaultproject"
- Name of addon is "provisioner-addon"
- The addon will be deployed to a namespace called "karpenter"
- You will be using the "nodepool.yaml" which is located in the folder "
/getstarted/karpenter/addon"
The following items may need to be updated/customized if you made changes to these or used alternate names.
- project: defaultproject
- namespace: karpenter
kind: AddonVersion
metadata:
name: v1
project: defaultproject
spec:
addon: provisioner-addon
namespace: karpenter
template:
type: NativeYaml
yamlFile: nodepool.yaml
- Open Terminal (on macOS/Linux) or Command Prompt (Windows) and navigate to the folder where you forked the Git repository
- Navigate to the folder "
/getstarted/karpenter/addon" - Type the command below
rctl create addon version -f nodepool-addon.yaml
If you did not encounter any errors, you can optionally verify if everything was created correctly on the controller.
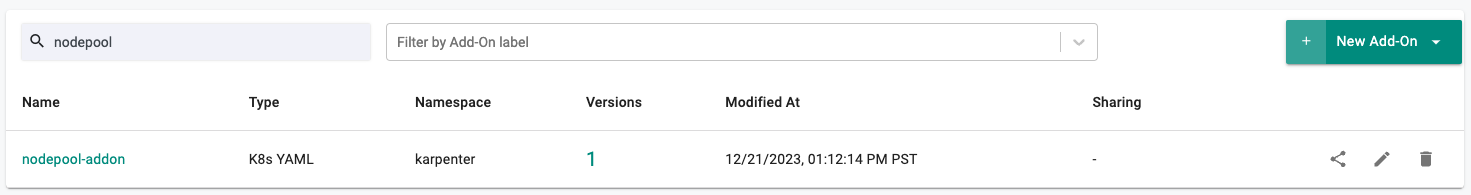
- Navigate to the "defaultproject" project in your Org
- Select Infrastructure -> Addons
- You should see an addon called "nodepool-addon"
Step 3: Create Blueprint¶
In this step, you will create a custom cluster blueprint with the Karpenter addon and the Nodepool addon. The "blueprint.yaml" file contains the declarative specification.
- Open Terminal (on macOS/Linux) or Command Prompt (Windows) and navigate to the folder where you forked the Git repository
- Navigate to the folder "
/getstarted/karpenter/blueprint"
The following items may need to be updated/customized if you made changes to these or used alternate names.
- project: "defaultproject"
apiVersion: infra.k8smgmt.io/v3
kind: Blueprint
metadata:
name: karpenter-blueprint
project: defaultproject
spec:
base:
name: minimal
type: custom
customAddons:
- name: karpenter-addon
version: v1
- name: nodepool-addon
version: v1
dependson:
- karpenter-addon
version: v1
- Type the command below
rctl apply -f blueprint.yaml
If you did not encounter any errors, you can optionally verify if everything was created correctly on the controller.
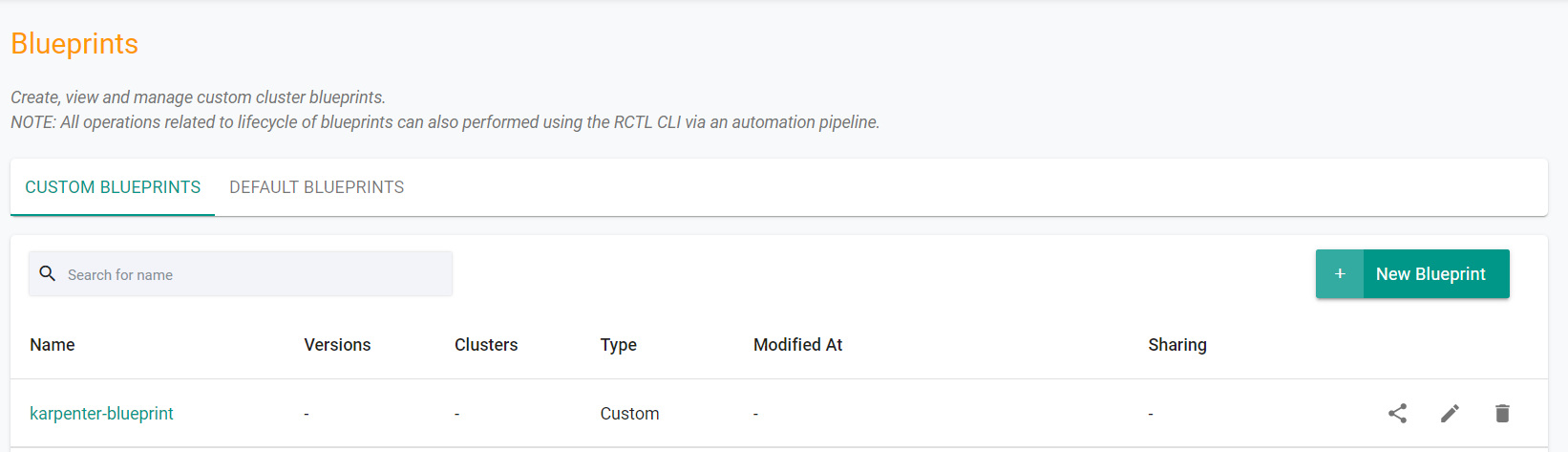
- Navigate to the "defaultproject" project in your Org
- Select Infrastructure -> Blueprint
- You should see an blueprint called "karpenter-blueprint
Step 4: Update Cluster Blueprint¶
In this step, you will update the cluster to use the previously created custom blueprint with the Karpenter addon and the Provisioner addon.
- Open Terminal (on macOS/Linux) or Command Prompt (Windows)
- Navigate to the folder "
/getstarted/karpenter/cluster" - Edit the blueprint section "cluster.yaml" file to use the newly created blueprint, update the blueprint name and add the version
apiVersion: infra.k8smgmt.io/v3
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: karpenter-cluster
project: defaultproject
spec:
blueprintConfig:
name: karpenter-blueprint
version: v1
cloudCredentials: aws-cloud-credential
config:
addons:
- name: kube-proxy
version: latest
- name: vpc-cni
version: latest
- name: coredns
version: latest
- configurationValues: |-
controller:
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: nodeInfra
operator: Exists
name: aws-ebs-csi-driver
version: latest
iam:
serviceAccounts:
- attachPolicy:
Statement:
- Action:
- ec2:CreateLaunchTemplate
- ec2:CreateFleet
- ec2:RunInstances
- ec2:CreateTags
- iam:PassRole
- iam:CreateInstanceProfile
- iam:TagInstanceProfile
- iam:AddRoleToInstanceProfile
- iam:RemoveRoleFromInstanceProfile
- iam:DeleteInstanceProfile
- ec2:DeleteLaunchTemplate
- ec2:TerminateInstances
- ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplates
- ec2:DescribeSpotPriceHistory
- ec2:DescribeImage
- ec2:DescribeImages
- ec2:DescribeInstances
- ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups
- ec2:DescribeSubnets
- ec2:DescribeInstanceTypes
- ec2:DescribeInstanceTypeOfferings
- ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones
- ssm:GetParameter
- eks:DescribeCluster
- pricing:DescribeServices
- pricing:GetAttributeValues
- pricing:GetProducts
- iam:GetInstanceProfile
Effect: Allow
Resource: '*'
Version: "2012-10-17"
metadata:
name: karpenter
namespace: karpenter
withOIDC: true
identityMappings:
arns:
- arn: "arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT-NUMBER>:role/KarpenterNodeRole-Rafay"
group:
- system:bootstrappers
- system:nodes
username: system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}}
managedNodeGroups:
- amiFamily: AmazonLinux2
desiredCapacity: 1
instanceType: t3.large
labels:
nodes: infra
maxSize: 2
minSize: 0
name: infra-nodegroup
taints:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: nodeInfra
version: "1.29"
metadata:
name: karpenter-cluster
region: us-west-2
tags:
cluster-name: karpenter-cluster
email: <EMAIL>
env: <ENV>
version: "1.29"
vpc:
autoAllocateIPv6: false
cidr: 192.168.0.0/16
clusterEndpoints:
privateAccess: true
publicAccess: false
systemComponentsPlacement:
nodeSelector:
node: infra
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: nodeInfra
operator: Exists
type: aws-eks
rctl apply -f cluster.yaml
If you did not encounter any errors, you can optionally verify if everything was created correctly on the controller.
- Navigate to the "defaultproject" project in your Org
- Select Infrastructure -> Clusters
- You should see the cluster is now using the "karpenter-blueprint
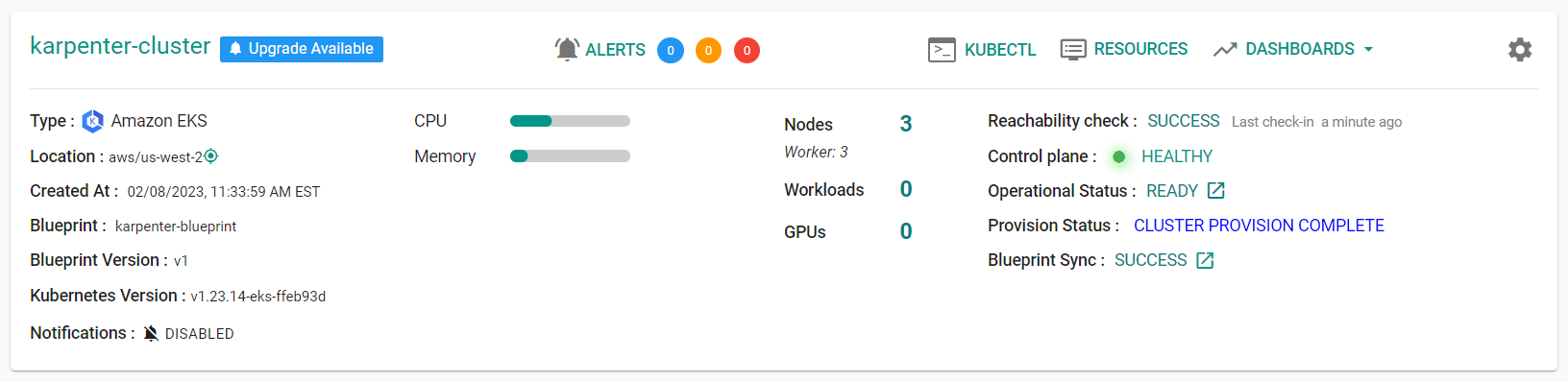
- Navigate to Infrastructure -> Clusters
- Click on "KUBECTL" in the "karpenter-cluster" cluster card
- Type the command below
kubectl get pods --namespace karpenter
- You should see a result like the following.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
karpenter-addon-5fc854c49f-h7pnj 1/1 Running 0 3m18s
Recap¶
As of this step, you have created a "cluster blueprint" with Karpenter and a NodePool/EC2NodeClass as addons, and applied this blueprint to the existing cluster. You are now ready to move onto the next step where you will deploy a test workload to scale the cluster with Karpenter.