Setup
What Will You Do¶
In this part, you will use the Platform Team persona (i.e. Infra Admin role in Rafay) to import and configure the environment manager resources.
Important
This is a one-time setup. Once completed, it can be shared/used by 100s/1000s of developers in your Org.
Step 1: Import Template¶
In this step, you will use the Loader Utility to import the Environment Manager templates needed for this environment.
- Follow the instructions here to use the loader utility
- When using the loader utility, be sure to uncomment the following template - ../terraform/jupyterhub in the templates section of the values.yaml file
Once Complete, you will see the new environment card in your organization under Environments -> Environments
Step 2: Configure Environment Contexts¶
In this step, you will configure the environment context in the controller with your Rafay account details. These account details will be used by Environment Manager to interact with your account.
Configure Rafay Context¶
You will use the CLI config details of your Rafay account to populate this context. The values needed can be found in a CLI config file. To obtain a CLI config file, navigate to Home -> My Tools -> Download CLI Config
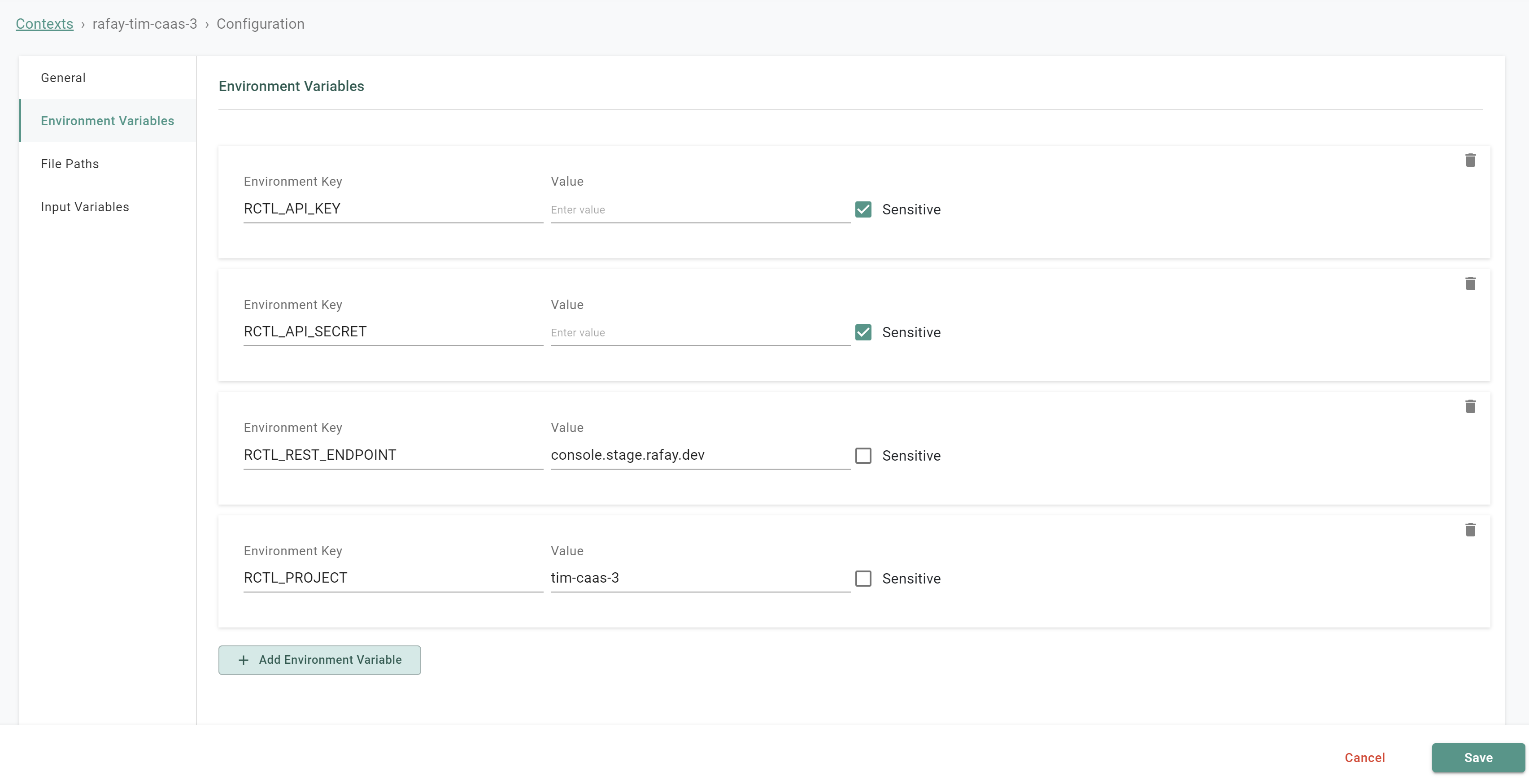
- Navigate to Environments -> Contexts
- Click on the existing Rafay context name
- Select Environment Variables
- Populate the API key, secret and endpoint variables (Note, the project variable is pre-populated for you)
- Ensure that you select the sensitive checkbox for both fields
- Click Save
Important
The Rafay agent automatically writes back the environment variables to Git. The resources (esp. secrets) you identify as sensitive. will be automatically encrypted using a secret sealer before being synced to your Git repo.
Step 3: Configure Template Variables¶
In this step, you will review the resource templates and environment templates to ensure that all variables are updated for your environment.
- Navigate to Environments -> Resource Templates
- Click on the resource templates that were created
- Click the view icon of the template version
- Verify all Input Variables
If any Input variables need to be modified, create a new version of the template with the modified variables. If a new version is created, be sure to update the Environment Template with any updated resource template versions.
- Navigate to Environments -> Environment Templates
- Click on the environment template that was created
- Click the view icon of the template version
- Verify all Input Variables
If any input variables need to be modified, create a new version of the template with the modified variables.
Recap¶
At this point, you have everything setup and configured to to allow self service of JupyterHub environments.