Part 2: Workload
What Will You Do¶
In this part of the self-paced exercise, you will deploy a Windows workload to the manged Windows node group on the EKS Cluster.
Step 1: Deploy Windows Workload¶
In this step, we will deploy a Windows workload into the previously created namespace.
- Navigate to the project in your Org where the cluster is located.
- Select Applications > Workloads
- Click "New Workload" > "Create New Workload"
- Enter "windows-workload" for the name
- Select "k8s YAML" for the Package Type
- Select "Upload files manually"
- Select the "Windows" namespace
- Click "Continue"
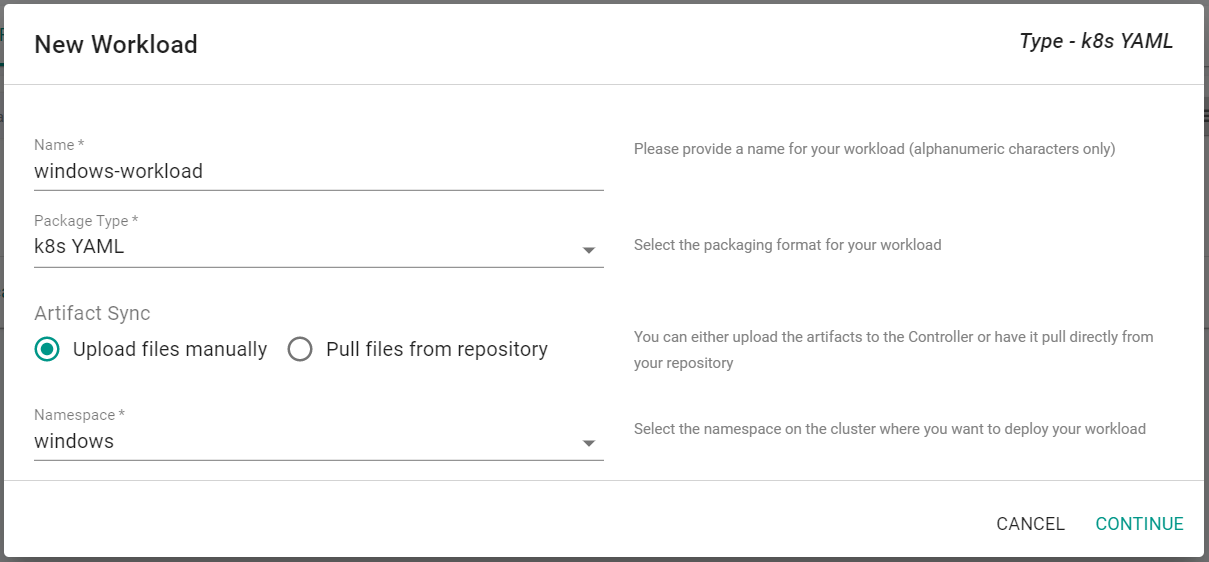
- Save the below specification file to your computer as "windows-workload.yaml".
Important
The 'nodeSelector' section, lines 31 & 32, specifies which OS to use. This is an important configuration to specify to avoid scheduling issues. Without a nodeSelector configuration, this deployment could be scheduled on a Linux node, causing it to fail. Kubernetes scheduling doesn't recognize Operating System, rather it is based on scores. For more information, please visit this URL.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: windows-server-iis-ltsc2019
namespace: windows
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: windows-server-iis-ltsc2019
tier: backend
track: stable
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: windows-server-iis-ltsc2019
tier: backend
track: stable
spec:
containers:
- name: windows-server-iis-ltsc2019
image: mcr.microsoft.com/windows/servercore/iis:windowsservercore-ltsc2019
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- powershell.exe
- -command
- "Add-WindowsFeature Web-Server; Invoke-WebRequest -UseBasicParsing -Uri 'https://dotnetbinaries.blob.core.windows.net/servicemonitor/2.0.1.6/ServiceMonitor.exe' -OutFile 'C:\\ServiceMonitor.exe'; echo '<html><body><br/><br/><H1>Windows Node Group Get Started!!!<H1></body><html>' > C:\\inetpub\\wwwroot\\iisstart.htm; C:\\ServiceMonitor.exe 'w3svc'; "
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: windows
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: windows-server-iis-ltsc2019-service
namespace: windows
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: windows-server-iis-ltsc2019
tier: backend
track: stable
sessionAffinity: None
type: LoadBalancer
- Click "Choose File" to upload the previously created YAML file
- Click "Save and Go To Placement"
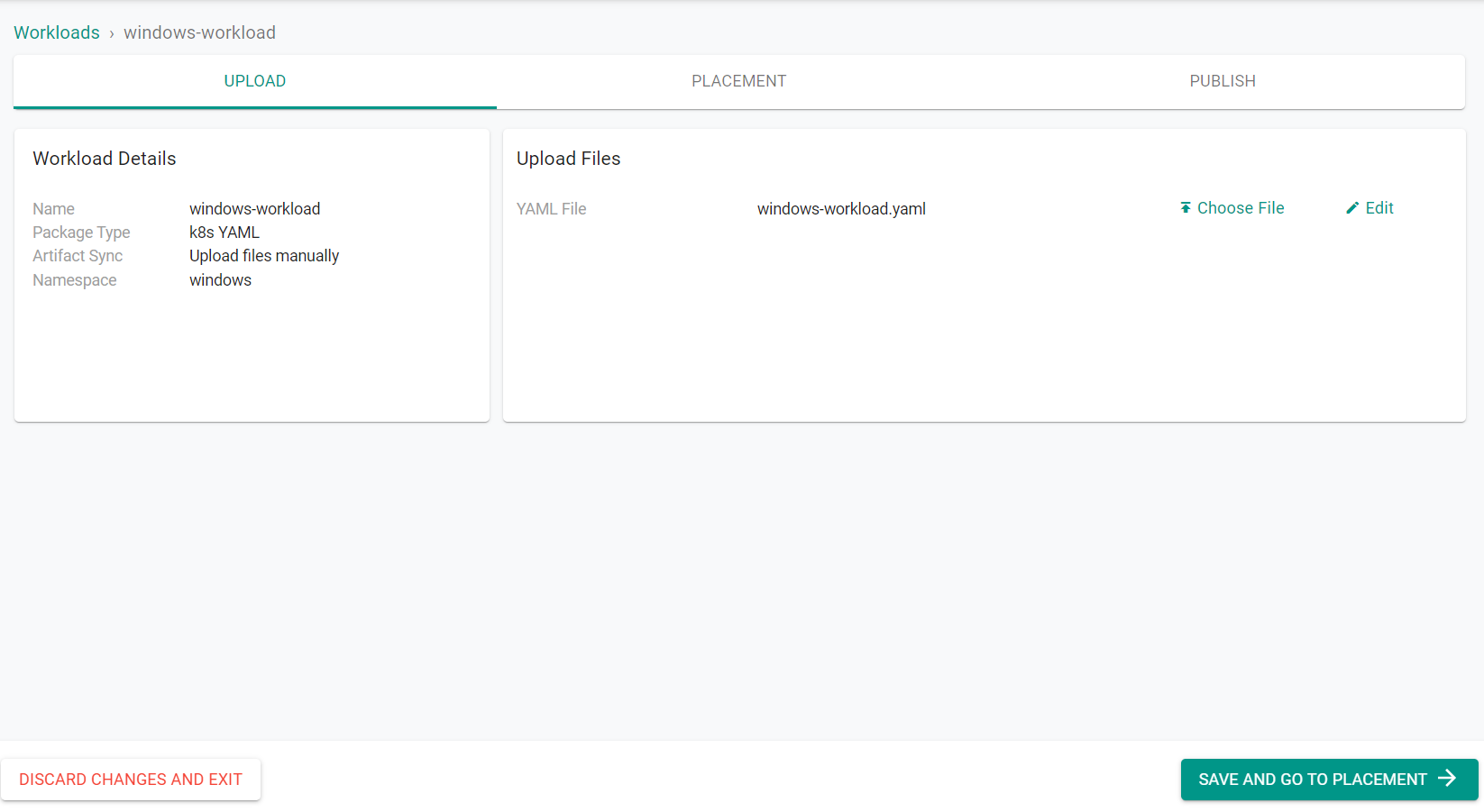
- Select the cluster to deploy the workload on
- Click "Save & Go To Publish"
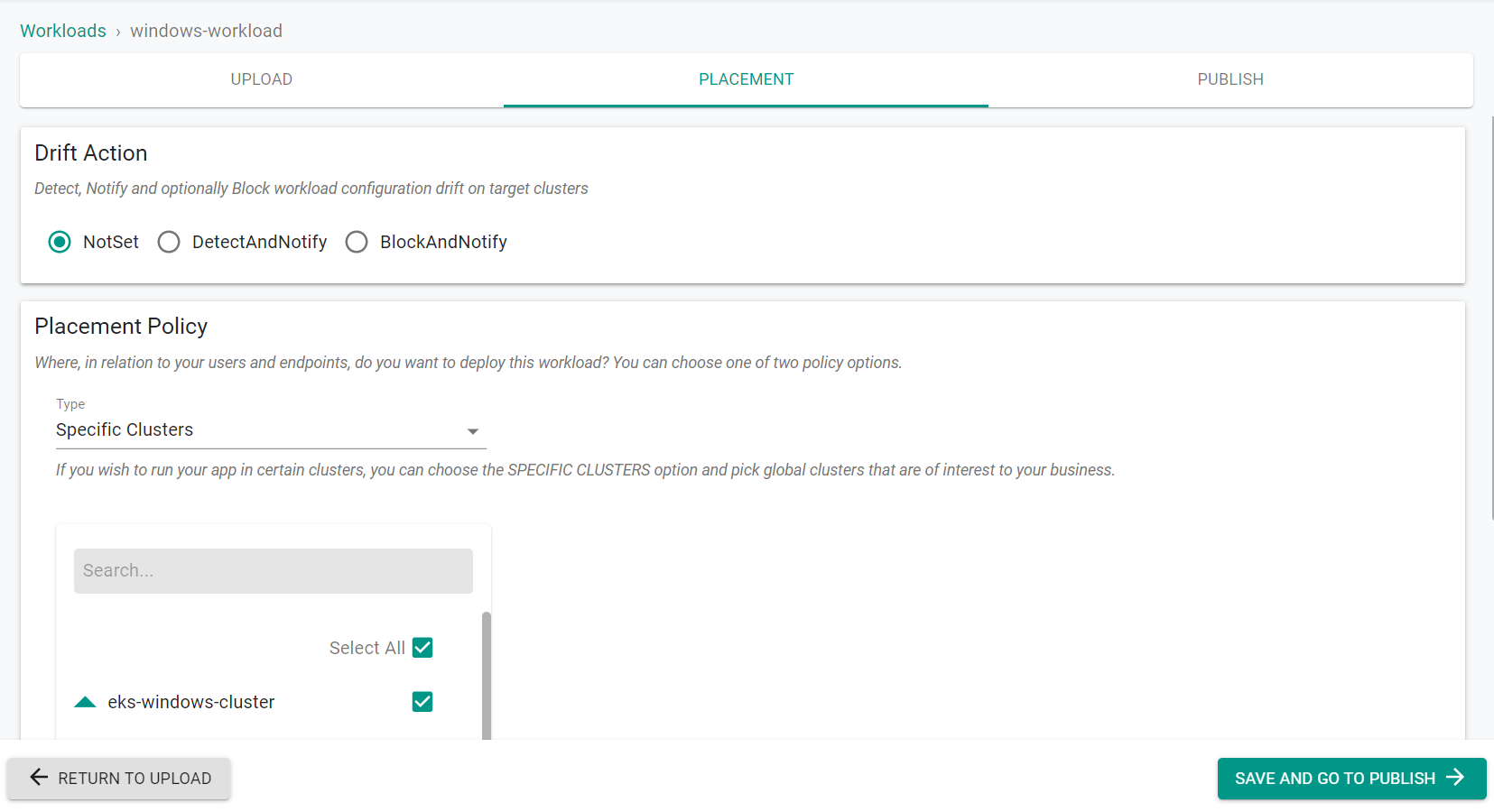
- Click "Publish"
The workload is now published on the cluster.
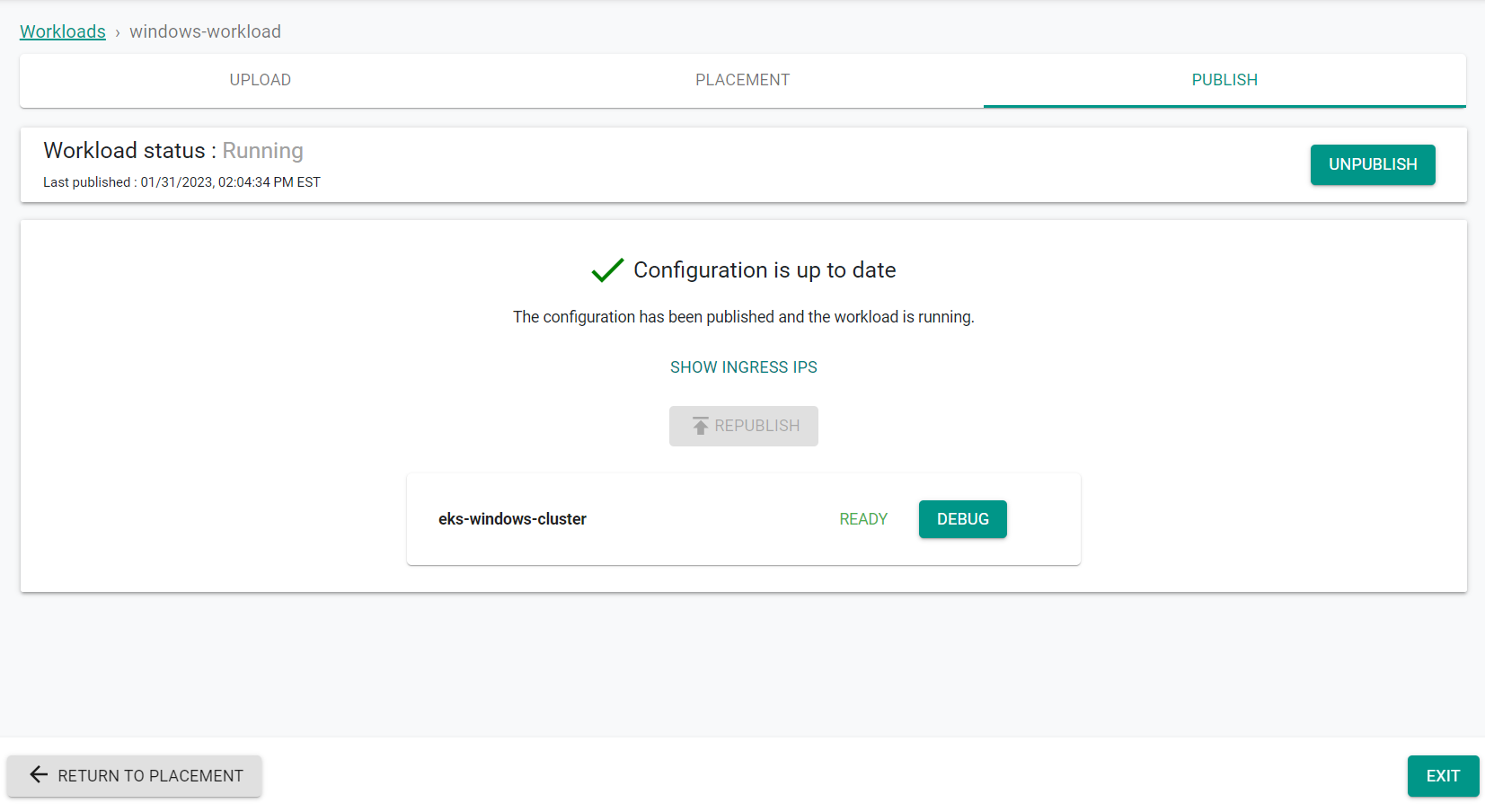
- Click "Exit"
Step 2: Validate Workload¶
In this step, we will verify the Windows workload is running and accessible.
- Navigate to the project in your Org where the cluster is located.
- Select Infrastructure > Clusters
- Click on the kubectl link of the cluster and type the following command
kubectl get pods -n windows
You should see output similar to the following showing the windows workload running
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
windows-server-iis-ltsc2019-7b985676f9-wpvbn 1/1 Running 0 13m
- Enter the following command
kubectl get services -n windows
You should see output similar to the following showing the external IP address of the workload.
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
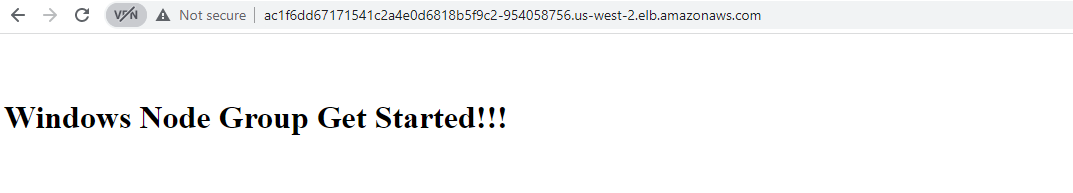
windows-server-iis-ltsc2019-service LoadBalancer 10.100.127.47 ac1f6dd67171541c2a4e0d6818b5f9c2-954058756.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com 80:32376/TCP 9m24s
- Enter the external IP address from the previous command into a web browser
You should see a response from the Windows web server workload.
Recap¶
Congratulations! At this point, you have successfully provisioned a Windows workload running on an Amazon EKS cluster with a managed Windows node group in your AWS account.